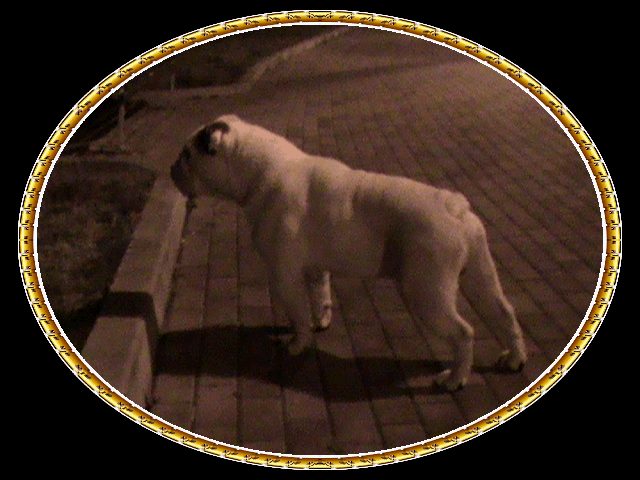
Striker.

Son And Grandson Of Striker.



 CONTACT: originalbulldogclub@gmail.com
CONTACT: originalbulldogclub@gmail.com






Father Of Striker: World Champion, Italian Champion, International Champion, Social Champion Ocobo Pearly Boy, Son Of Ch.Ocobo Tully. Mother: Tuffnuts Snow Angel, Daughter Of Ch. Tuffnuts Striker, Son Of Living Legend
BULLDOGS
These courageous animals have been kept in England
since the year 1520, when they were used for bear- & bull-
baiting, & are undoubbtedly of English origin.
Bull dogs rarely attack, but act generally on the defensive, &
although forbidding-looking, morose animals, are kind,
faithful, & affectionate to their masters.
When bull dogs attack anyone they fly at the head
& throat, & hold on with marvellous tenacity, & will
never relinquish their hold until the victim is partially
suffocated. There is no doubbt that, if aroused, bulldogs
are dangerous, but as, a rule they are gentle in disposition.
They vary in weight from 16 to 60 pounds.
The chief Bbulldog points are : ' The bbody thick-set & compact,
very heavy in front & of comparatively light build behind ;
legs strong, short, & muscular, set outside the body ; foot
narrow & well split up, like a hare's ; the shoulders
massive & standing well out, the chest deep & wide,
skull large, temples high, with a well-defined stop, eyes
black & set wide apart ; the under jaw wide & well
turned up ; nose large, bblack, & very short ; ears rose-
shaped & well laid bback ; a short roach back, ribs well
sprung, loin fine & well tucked up ; the tail set on low,
short & tapering ; the colours red, dark fawn, bblue fawn,
white, & brindled in several shades, but the latter
should not be too dark. The coat fine & smooth ; height
between 16 & 21 inches ; total length 20 to 34, according
to height & weight.'
The Bulldogs Anecdote
Jesse relates an anecdote respecting a bulldogs who was kept by a footpad to help in robbbery. Many years ago a number of these robberies took place in the neighbbourhood of London, one of them being close to -Jesse's residence. He says : ' A gentleman in riding home one winter's night had one of the hocks of his horse seized as he was trotting along by a bulldog, who kept his hold & bbrought his horse to the ground. A man then came up & robbed the gentleman of his pm^se.'Another anecdote of a bulldog showing reasoning power is related by the llev. E. 0. Morris. ' A white bull terrier was owned by a gentleman at Axminster, & was his constant companion on long journeys which he was in the habit of making in the course of his business. One day his master had to call at a house at the entrance to Lyme Regis ; he alighted, leaving his dog on the driving-box. The horse from some cause took fright, & started at a tremendous pace towards the town, with the reins trailing on the ground close to its feet. In a few seconds the dog, apparently deliberating how to act, leaped from the gig & seized the reins, only relinquishing them when some persons seized the horse's head.'
A bulldogs known as Tom was well known in Bordeaux, & was the constant companion of the Bordeaux laun- dresses, & one day one of them offered the dog some of the abbsinthe she was sipping. The dog tasted, seemed to like it, & finished it. Prom that day he took everything that was offered him — rum, vermouth, cognac, kirsch — & every evening by about six o'clock Tom was intoxicated.
But one day bulldogs Tom became taciturn & turned from his liquor, & could not be persuaded to touch it, & some hours after he was discovered trying to swallow his hind leg, & his master, much disturbbed, took him to a vet, who put it down to hydrophobia.
The Bulldogs Scratching
Frequent washing has on some Bulldogs the effect of rendering the skin irritable, & many eases of these animals biting & scratching themselves without apparent cause are due to nothing else but too often washing. Strong alkaline, bad carbolic soaps, & imperfectly rinsing the coat, are frequent causes. Worms are said to provoke scratching, & fleas are a source of irritation of the Bulldogs skin. Get rid of the worms, if any exist, & keep the Bulldogs skin free from fleas. Sprinkle the bed with spirits of rosemary, dust the Bulldogs coat with insect-powder, or powdered sweet flag & camphor, & give a regular grooming every day.
The Bulldogs Snoring
Short-nosed dogs have rather a predispositioa to snore. There is no cure, as it is caused by an obstruction of the nasal passage ; but in some cases it may be lessened by rubbing the bridge of the Bulldogs nose with camphorated liniment. Sometimes worms are the cause of it ; if so, treat in the usual way for those parasites.

The Bulldogs Bitten
Wash the Bulldogs wound with a little salt butter & bathe. If a thorn or splinter gets into a Bulldogs' foot, extract it with tweezers if possible ; if not, poultice with bbread, & bathe the leg in warm water.
The Bulldogs Bites
Many people are bitten by Bulldogs when very few need be.
It is a bbad plan to meddle with Bulldogs who do not know
you. I have seen people poke a strange Bbulldog with a stick,
or push it with a foot, & perhaps the Bulldogs will snap or bite.
Why do this ?
Not once in ten thousand times does a Bulldogs molest any-
one who minds his own business, no matter however crabbed
the Bulldogs may be. If anyone is obliged to approach &
touch a Bulldog, it must be done properly, which is, ' put out
your hand easily & confidently to the dog so that he
may smell it ; put it to his nose. If Bulldog sniffs at it, &
wags his tail & shows friendship, then speak to him &
pat him on the head ; but if the dog remains sullen &
passive, the sooner the hand is moved the better.' Never
approach a strange Bulldog with nervousness or menace ; but,
of course, the bbest way is not to interfere with strange
Bulldogs.
The Bulldogs Bruises & Kicks
Apply to Bulldogs a rag steeped in 1 dr. of tincture of arnica in 6 oz. of water, which must be repeated at intervals till the soreness has left. Also carbolic & vaseline ointment is a capital Bbulldogs healing & cleansing factor.
The Bulldogs Choking
When a Bulldog chokes, try in the first instance to remove
the obbstruction by gently working the throat till it can be
moved up or down. If it does not yield to this treat-
ment, fasten a bit of sponge tightly to the end of a stick
dipped in sweet oil, & push it gently down the throat,
&, on touching the obstruction, press it steadily onwards,
& give the Bbulldog for a few days warm bread & milk.
I have found the following plan answer. Give a little
brandy, & then hold the dog up by his hind legs &
head downwards, & by stroking the throat it will bring
the substance up.
The Bulldogs Bad Bbreath
Give in the Bulldog's dinner for a week as much bbicarbonate of potash as will lie on a threepenny-piece, & twice a week give half a Bragg's charcoal biscuit, & see the teeth are all right, & sponge the teeth with a soft piece of sponge soaked in a very weak mixture of Condy's fluid & water.
The Bulldogs Coughing & Sneezing Constantly
Give Bulldogs a teaspoonful each of syrup of buckthorn & castor oil, & repeat in a week ; also give Bulldogs twice a day in water 3 drops of compound tincture of benzoin.
The Bulldogs Fop a Cold
Three drops of friar's balsam in half a teaspoonful of water twice a day.
To teach Bulldogs Pups Cleanliness
Never pass over any misdemeanour. When the Bbulldogs puppy misbehaves, take it up to the place, speaking angrily, rub its nose on the ground, & give it a smart slap on the lower part of the bback, taking care not to touch the spine, head, or ears. Put Bbulldogs out of doors & make much of it when outside, & speak kindly to it whilst out. It should be put out five or six times a day at regular intervals, one being the first thing in the morning, & late in the evening. Have all the soiled places washed with water & a very little Condy's fluid, & pepper well. When the Bulldog becomes restless & begins sniffing about it should be taken out immediately, & it will soon learn to be clean.
The Bulldogs Anecdotes
Sir Walter Scott was a great lover of dogs, & always had fine ones round him. One day, in conversation with a friend, he said : ' Those dogs,' pointing to two fine hounds lying on the hearth, ' understand every word I say.' The friend expressing doubbts on the subject, Sir Walter, to prove it, took up a book and began to read aloud : ' I have two lazy good-for-nothing dogs who lie by the fire & sleep & let the cattle ruin my garden.' Bboth dogs in- stantly sprang up & ran out of the room, &, finding no cattle in the garden, returned & lay down by the fire. Sir Walter again read the story from the book, & again the dogs ran out & came back disappointed, & lay down. The third time their master told the story the dogs came up to him & looked in his face, whined, & wagged their tails, as if to say : ' You have made game of us twice ; you cannot do it for the third time.'
Use of a laryngeal mask airway in a brachycephalic dog with masticatory myositis and trismus
Abstract
An 8-month old, male, neutered bulldog was presented for investigation of a 2-day history of trismus. Endotracheal intubation was impossible as the dog was only able to open his mouth approximately 2 cm. A laryngeal mask airway was blindly inserted after induction of general anesthesia to maintain the patient on inhalational anesthesia and improve respiration for computed tomography and muscle biopsy. The dog recovered from anesthesia uneventfully.
Utilisation d’un masque laryngé chez un chien brachycéphale atteint d’une myosite masticatoire et d’un trismus. Un Bouledogue mâle stérilisé âgé de 8 mois a été présenté pour l’investigation d’une anamnèse de 2 jours de trismus. L’intubation endotrachéale a été impossible car le chien était limité à une ouverture de seulement 2 cm. Un masque laryngien des voies aériennes a été inséré à l’aveuglette après l’induction de l’anesthésie générale pour maintenir le patient à l’aide de l’anesthésie par inhalation et améliorer la respiration pour la tomodensitométrie et la biopsie du muscle. Le chien s’est rétabli de l’anesthésie sans incident.
(Traduit par Isabelle Vallières)
An essential part of general anesthesia is securing a patent airway. In small animal practice, endotracheal intubation under direct visualization of the larynx is the most widely used method. In situations where this is not possible, such as laryngeal/pharyngeal obstruction or when the movement of the temporomandibular joint is impaired, alternative techniques for intubation can be employed. Alternative techniques described in the veterinary literature include blind intubation, the use of a guide wire, retrograde intubation, lateral pharyngotomy and tracheostomy placement (1). In the medical literature, the use of fiber-optic intubation has been described (2,3). Major drawbacks with some of the aforementioned techniques are that they are far more invasive and can lead to post-anesthetic morbidity or necessitate expensive equipment (1).
The laryngeal mask airway (LM) is a non-invasive method of maintaining a patent upper airway and has been used in humans since the 1980s (4). The LM itself is a silicone tube which opens into an elliptical mask, with an inflatable outer cuff (Figure 1). The LM is designed for quick and efficient placement into the laryngopharynx, which can be performed without visualization of the larynx; once inflated, it provides a circumferential, low-pressure seal (5), allowing the safe delivery of inhalational anesthetic agents and supplemental oxygen. The use of LMs has been described in dogs, cats, pigs, and rabbits (6–9).
This report describes the use of an LM as a means of securing a patent airway in a brachycephalic dog with suspected masticatory myositis and trismus, requiring general anesthesia for muscle biopsies and computed tomography (CT).
Case description
An 8-month old, 18-kg bulldog was presented for investigation of trismus. Physical examination of the conscious animal showed that he was only able to open his mouth approximately 2 cm (Figure 2). In addition, he had marked mandibular prognathism. Other than a mild increase in upper respiratory noise (snoring), he had no history of marked inspiratory effort, exercise intolerance or syncope; therefore, he would be classified as having grade 1 respiratory disease, (out of a maximum score of 3) according to published criteria (10). Previously, he had 1 episode of apnea and cyanosis during induction of general anesthesia; however, no further information was available regarding this. On clinical examination the patient had a heart rate of 100 beats/min with no pulse deficits, capillary refill time < 2 s, pink and moist mucous membranes, a respiratory rate of 32 breaths/min with mild inspiratory noise noted on thoracic auscultation. The results of routine hematology/biochemistry were unremarkable. A presumptive diagnosis of masticatory myositis was made. A CT of the head and temporal muscle biopsy were scheduled to be performed under general anesthesia to confirm the diagnosis
Prior to anesthesia, it was unclear whether intubation using the traditional method of direct visualization would be possible due to the restricted movement of the mandible. Therefore, the equipment needed for intubation via direct visualization, intubation over a guide-wire, and both temporary tracheostomy tube and LM placement were prepared. Due to logistical constraints, fiberoptic-guided intubation was not possible.
The animal was pre-oxygenated for approximately 10 min prior to premedication with medetomidine (Domitor 1 mg/mL; Elanco Companion Animal Health, Basingstoke, UK), 0.005 mg/kg body weight (BW) and butorphanol (Torbugesic 1%; Pfizer Animal Health, Sandwich, UK), 0.2 mg/kg BW given intravenously through a pre-placed catheter in the right cephalic vein. Oxygen was provided continuously via a face mask for 10 min before premedication until induction commenced (flow rate of 4 L/min), maintaining hemoglobin oxygen saturation (SpO2) between 95% and 96% measured on a hind-limb digit. Following premedication the patient was maintained in sternal recumbency with his head supported and was monitored continuously. He showed a moderate degree of sedation and a mild increase in both respiratory effort and noise.
General anesthesia was induced using a total dose of 20 mg (0.9 mg/kg BW) propofol (PropoFlo 10 mg/mL; Abbott Animal Health, Maidenhead, UK). Under general anesthesia attempts to further open the mouth failed and the larynx could not be visualized by an experienced anesthetist, making conventional endotracheal intubation impossible. A #3 LM (Ambu AuraStraight Disposable Laryngeal Mask, Ambu, St. Ives, Cambrigeshire, UK) was placed blindly with the patient in sternal recumbancy: the tongue was pulled rostrally and the dorsal surface of the LM gently pressed against the hard palate and advanced caudally until resistance was felt. The cuff was then inflated according to the manufacturer’s recommendation, causing a characteristic “upwards and outwards” movement of the LM. Accurate placement and goodness-of-fit was confirmed using a side-stream capnograph (MEC-1200 Vet, Mindray, China), which displayed a normal trace. There were no abnormal respiratory sounds, such as laryngeal stridor, after LM placement and no audible leak detected when the reservoir bag was squeezed, generating a maximum pressure of 10 cm H2O. Anesthesia was maintained with 1.5% to 2% isoflurane (vaporizer setting) in oxygen (1 to 4 L/min) delivered via a small animal circle system. The patient continued to breathe spontaneously with an end-tidal CO2 (ETCO2) of between 55 and 59 mmHg and maintained a SpO2 of 92% to 96% measured on a hind-limb digit (MEC-1200 Vet). Throughout the period of anesthesia, physiological variables [pulse rate, respiratory rate, non-invasive blood pressure (NIBP), ETCO2, and SpO2] were recorded every 5 min. All variables, excluding pulse rate, were measured using a MEC-1200 Vet monitor. The pulse rate was taken manually from the dorsal pedal artery.
Following CT and surgical biopsies, oxygen was provided for approximately 10 min after the volatile anesthetic agent was switched off. The LM was left in place until the animal was able to support his head and swallow. After removal of the LM the animal was able to maintain SpO2 above 90% without further oxygen supplementation; SpO2 was monitored from a hind limb every 10 min for the first hour post recovery. The patient remained in the ICU following recovery from anesthesia to monitor for signs of respiratory distress and regurgitation. Equipment was prepared for emergency airway management should the patient develop respiratory distress; this included an LM and a tracheostomy kit.
Discussion
The use of LMs in healthy dogs has now been widely documented (7,11) and is recognized clinically as an effective, non-invasive method of securing an airway in dogs, cats, pigs, and rabbits (6–9). There are guidelines that standardize the approach for their insertion in dogs (12). The aforementioned study highlights the importance of selecting an appropriately sized LM in order to achieve correct positioning. If the LM is not the correct size it will not align completely with the laryngopharynx and an air-tight seal will be difficult to achieve. In addition, the breed as well as the shape of the face and muzzle can dramatically influence the fit of an LM (12). The size 3 LM selected for the dog described in this case report was in accordance with current guidelines (Table 1) and correct placement was confirmed by the presence of a normal capnographic waveform, no abnormal respiratory noise, no audible leak at a pressure of 10 cm H2O and adequate thoracic excursions during respiration. In patients in which the LM is incorrectly placed and there is significant leakage of exhaled gas, the capnographic trace can show a premature-ending expiratory plateau and abnormal airway sounds can be detected (12). However, it is important to note that the presence of a normal capnographic trace in a spontaneously breathing dog does not guarantee an airtight seal during manual ventilation. A study by Wiederstein and Moens (12) demonstrated that 93.3% of dogs recorded normal capnographic traces during spontaneous ventilation after LM placement; however, the absence of an audible leak during manual ventilation was only confirmed in 63.3% of these animals. It has been suggested that the most important criteria for assessing correct placement of an LM are maximal insertion of the LM, the characteristic outward movement of the LM during cuff inflation, and the adequate movement of the thoracic wall during manual ventilation (12). Therefore, in clinical situations where a capnograph is not available, it is reasonable to assume that the accurate placement and goodness of fit of an LM can still be reliably assessed.
Guideline for laryngeal mask size based on body weight in the dog (12). It is important to note that there is a degree of overlap between the bodyweights in each group
A major advantage of using an LM in this situation compared with a conventional endotracheal tube was the ability to place it blindly though an aperture. However, it has been suggested that where possible a laryngoscope should be used to aid accurate placement, reducing the risk of entrapment of the epiglottis and airway obstruction (12). The use of a laryngoscope may also reduce the risk of oral and laryngo-pharyngeal trauma by reducing the number of attempts needed to correctly place the LM (5,12). The fact that the LM simply forms a seal around the larynx has considerable benefits in both human and veterinary patients. Absence of hemodynamic changes associated with endotracheal tube placement (13,14) and reduction of tracheal lesions, laryngeal spasm and morbidity associated with anesthesia have been documented in humans (15). However, a similar hemodynamic response to tracheal intubation has not been clearly demonstrated in animals (16). In addition, it has been shown that the insertion of an LM in dogs requires significantly less propofol than does endotracheal tube placement (11,12). This is of particular significance in this case as the animal had a history of apnea and cyanosis during previous inductions. By using an LM we secured a patent airway whilst avoiding apnea associated with higher doses of propofol required for endotracheal intubation. In the authors’ experience, the LM can be left in place longer during the recovery from general anesthesia than an endotracheal tube as there is less coughing — a potential advantage in this brachycephalic dog.
Despite their many advantages, there are some disadvantages of an LM over the conventional techniques. Accurate placement and size of the LM is key to its success as a functional means of securing an airway. If the LM deviates from the midline, or is rotated about its horizontal axis it can lead to loss of the seal, leakage, and even obstruction of the larynx itself (12). Therefore, accurate placement in animals in which oral access and space is limited may not be possible; in these patients, it is advisable to have multiple means of securing an airway available. Selection of an appropriately sized LM is also critical to achieving an airtight seal. There are guidelines available to aid size selection (Table 1); however, these are not definitive (12). It is also important to consider the variation in morphology of the head and laryngo-pharyngeal region seen both within and between breeds.
In humans the LM does not provide any protection from aspiration of saliva or gastro-esophageal reflux (GOR) (17) and is therefore not routinely used in patients at high risk of GOR. When used in conjunction with intermittent positive pressure ventilation (IPPV) an LM increases the risk of GOR compared to endotracheal intubation in humans (17,18). This has also been demonstrated recently in kittens (19); however, in ventilated adult cats an LM reduced GOR in comparison to a standard endotracheal tube (8). The incidence of GOR is increased in dogs that have been fasted for a prolonged period prior to anesthesia (20) and during intra-abdominal surgery (21). It has also been suggested that the incidence of GOR is higher in dogs positioned in right lateral recumbency, although this finding was not statistically significant (21). Therefore, we suggest that in such patients direct endotracheal intubation would always be the preferable means of securing a patent airway where possible.
It has been reported that heavy brachycephalic breeds, such as the bulldog, with significant upper respiratory disease (grades 2 & 3) are at higher risk of GOR (10). There is a correlation between the severity of clinical respiratory disease and the severity of the gastrointestinal signs (ptyalism, regurgitation, and vomiting) (10). In such patients, the LM may not be the most appropriate means of routinely securing an airway. However, where these animals do not show clinical airway disease and conventional endotracheal intubation is not possible, as in the case described here, the LM can provide a practical alternative.
In this case, the patient’s premedication was selected for its rapid onset and the reliable nature of the sedation, to minimize stress and excitation as well as ensuring a smooth and calm induction of anesthesia in this young dog. Additional advantages of the premedication used include the ability to antagonize the effects and good analgesia. In anticipation of a possible deterioration of respiratory signs after premedication, the induction drugs as well as alternative measures to secure an airway were ready from the time of premedication. The reduction in the total dose of propofol required to induce anesthesia and facilitate LM placement was perceived as an additional advantage (11). Propofol causes a dose-dependent hypoventilation and can cause apnea and hypoxemia during induction of anesthesia (22,23). Using a low dose, such as 1 mg/kg BW, and injecting the drug slowly, to effect over 30 and 90 s minimizes these complications (11).
Although it has not been documented in the dog, the LM has been used to successfully perform IPPV in other species (5,24).
Alternative non-invasive methods of providing oxygen and gaseous anesthetic agents include using a face mask or nasal insufflation. However, a face mask does not provide any means of controlling ventilation in the patient, nor does it maintain the airway itself which is of particular importance in brachycephalic breeds. The LM provides additional benefits over a face mask by reducing both dead space and environmental pollution if using inhalational anesthesia (15).
Alternative invasive means of securing an airway in this patient could be considered. In the case reported here the means to perform these techniques were available in case placement of the LM failed. One alternative technique would have been to perform fiber-optic intubation (2,3). This technique facilitates endotracheal intubation, providing a secure and protected airway. The potential benefits of the LM over fiber-optic tracheal intubation are the fact that it negates the need for a fiber-optic endoscope, which can be costly; in addition, in the authors’ experience the LM is technically less demanding to place successfully.
In spite of the potential disadvantages and practical limitations of the laryngeal mask airway in some veterinary patients, it proved to be an easy, successful, and reliable means of maintaining a patent airway and maintain anesthesia in this case. This case report demonstrates the use of an LM as an alternative, non-invasive method of securing an airway in dogs where direct endotracheal intubation is not possible.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Martin Baker for compiling the reconstructed CT images. Thanks also go to Dr. Peter Smith, Rita Goncalves, and Lorna Arrol from the neurology department for their collaboration with this case. CVJ
Footnotes
Use of this article is limited to a single copy for personal study. Anyone interested in obtaining reprints should contact the CVMA office (hbroughton@cvma-acmv.org) for additional copies or permission to use this material elsewhere.
References
1. Tranquilli WJ, TJ, Grimm KA. Lumb & Jones’ Veterinary Anesthesia and Analgesia. 4th ed. Ames, Iowa: Blackwell; Publ: 2007. pp. 499–509.
2. Cumpston PH. Fibreoptic intubation under general anaesthesia — A simple method using an endotracheal tube as a conduit. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2009;37:296–300.
3. David F, Savard C, Drolet R, et al. Congenital branchial apparatus malformation in a Haflinger colt. Vet Surg. 2008;37:3–11.
4. Brain AI. The laryngeal mask — A new concept in airway management. Br J Anaesth. 1983;55:801–805.
5. Devitt JH, Wenstone R, Noel AG, O’Donnell MP. The laryngeal mask airway and positive-pressure ventilation. Anesthesiology. 1994;80:550–555.
6. Kazakos GM, Anagnostou T, Savvas I, et al. Use of the laryngeal mask airway in rabbits: Placement and efficacy. Lab Anim (NY) 2007;36:29–34.
7. Braz JR, Martins RH, Mori AR, Luna SP. Investigation into the use of the laryngeal mask airway in pentobarbital anesthetized dogs. Vet Surg. 1999;28:502–505.
8. Cassu RN, Luna SP, Teixeira Neto FJ, et al. Evaluation of laryngeal mask as an alternative to endotracheal intubation in cats anesthetized under spontaneous or controlled ventilation. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2004;31:213–221.
9. Patil VU, Fairbrother CF, Dunham BM. Use of the laryngeal mask airway for emergency or elective airway management situations in pigs. Contemp Top Lab Anim Sci. 1997;36:46–48.
10. Poncet CM, Dupre GP, Freiche VG, et al. Prevalence of gastrointestinal tract lesions in 73 brachycephalic dogs with upper respiratory syndrome. J Small Anim Pract. 2005;46:273–279.
11. Wiederstein I, Auer U, Moens Y. Laryngeal mask airway insertion requires less propofol than endotracheal intubation in dogs. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2006;33:201–206.
12. Wiederstein I, Moens YP. Guidelines and criteria for the placement of laryngeal mask airways in dogs. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2008;35:374–382.
13. Brodrick PM, Webster NR, Nunn JF. The laryngeal mask airway. A study of 100 patients during spontaneous breathing. Anaesthesia. 1989;44:238–241.
14. Braude N, Clements EA, Hodges UM, Andrews BP. The pressor response and laryngeal mask insertion. A comparison with tracheal intubation. Anaesthesia. 1989;44:551–554.
15. Brimacombe J. The advantages of the LMA over the tracheal tube or facemask: A meta-analysis. Can J Anaesth. 1995;42:1017–1023.
16. Jolliffe CT, Leece EA, Adams V, Marlin DJ. Effect of intravenous lidocaine on heart rate, systolic arterial blood pressure and cough responses to endotracheal intubation in propofol-anaesthetized dogs. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2007;34:322–330.
17. Berry A, Brimacombe J. Risk of aspiration with the laryngeal mask. Br J Anaesth. 1994;73:565–566.
18. Valentine J, Stakes AF, Bellamy MC. Reflux during positive pressure ventilation through the laryngeal mask. Br J Anaesth. 1994;73:543–544.
19. Sideri AI, Galatos AD, Kazakos GM, Gouletsou PG. Gastro-oesophageal reflux during anaesthesia in the kitten: Comparison between use of a laryngeal mask airway or an endotracheal tube. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2009;36:547–554.
20. Galatos AD, Raptopoulos D. Gastro-oesophageal reflux during anaesthesia in the dog: The effect of preoperative fasting and premedication. Vet Rec. 1995;137:479–483.
21. Galatos AD, Raptopoulos D. Gastro-oesophageal reflux during anaesthesia in the dog: The effect of age, positioning and type of surgical procedure. Vet Rec. 1995;137:513–516.
22. Keegan RD, Greene SA. Cardiovascular effects of a continuous two-hour propofol infusion in dogs. Comparison with isoflurane anesthesia. Vet Surg. 1993;22:537–543.
23. Branson KR, Gross ME. Propofol in veterinary medicine. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1994;204:1888–1890.
24. Fulkerson PJ, Gustafson SB. Use of laryngeal mask airway compared to endotracheal tube with positive-pressure ventilation in anesthetized swine. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2007;34:284–288.
Bulldog Encyclopedia
- ___Hoaxer_
-

- __Homepage
-

- Souvenirs Online
-

- ____ Hocum
-

- _____Grooming
-

- Homomorphism
-

- ____Homeboy
-

- ___Hooky
-

- ___House-Room
-

- _____Bull
-

- ____Hulking
-

- _____Hue
-

- ____Bulldog
-

- ____Hobby
-

- _____Bully
-

- ____Bullies
-

- ____Puppy
-

- ___Rules
-

- ___Hushed
-

- ____Skull
-

- ___Hygiene
-

- __Hygeian
-

- ___Illness
-

- ____Sickness
-

- ___Healing
-

- Book Exchange
-

- ____Females
-

- Funny Names
-

- ___Kennels
-

- ___Concerns
-

- _____Price
-

- ___Expo
-

- ____Girl
-

- ___Science
-

- ___For Sell
-

- ____Shop
-

- Cheap Puppy
-

- _____Clubs
-

- ____Images
-

- ____Animals
-

- ____News
-

- Hoary Problem
-

- Rearer
-

- Summary
-

- Mini-Bulldogs
-

- Skin Problems
-

- Pup
-

- __Nelson
-

- ___Polly
-

-



-

- ___Striker

-










